Fresh Stem Cell TherapyAbout Fresh Stem Cell Therapy
Fresh stem cells are fresh cells immediately after harvesting, which maximizes the function of adipose stem cells.
Because the cells are used immediately for treatment without cryopreservation, their vitality can be maintained.
Major Advantages of Fresh Stem Cell Therapy
Fresh stem cell therapy maximizes cellular activity,
Because it is used immediately for treatment without cryopreservation, it is possible to maintain its vitality.
Recent studies have reported that the use of fresh stem cell therapy at the beginning of treatment is more likely to be highly effective,
This has led to early recovery and improved treatment success rates.
Advantages of Fresh Stem Cell Therapy
| Use of cells as they are | In tissue culture, cells are isolated and cultured in an artificially controlled environment, which may alter their original properties and characteristics, whereas in the non-culture method, adipose tissue-derived stem cells are used without artificial manipulation. |
|---|---|
| Real-time cell administration | Because cells are isolated fresh and used in real time, they retain their original functions. In the culture method, on the other hand, there are many molecular changes and reproduction of cells as they grow and age. |
| Automated treatment process | Tissue culture involves many manual processes, which can lead to risks such as contamination, differences in technique between workers, and mistaken specimens. The non-culture method used by our clinic is handled in a fully automated, closed system. |
| Short cell conditioning time | Adjustment time from cell extraction to administration at our clinic can be as short as 90 minutes. On the other hand, with the cell culture method, it may take several weeks to reach the target cell count in culture. |
Treatment of Diseases with Stem Cells
Although scientific and medical advances have increased the average life expectancy, it has not reached the level of healthy life expectancy where people can enjoy a high quality of life and live comfortably. Many people suffer physically and mentally from the diseases and disabilities associated with aging.
Today, more important than living longer is precisely "healthy aging" (Well Aging).
The key to solving this problem is precisely stem cells.
Stem cells are differentiated cells that have the ability to differentiate into various types of cells such as brain, skin, cartilage, bone, nerve cells, muscle cells, and immune cells and grow into body tissues. With the ability to replicate themselves and differentiate into tissue cells when needed, they can treat many diseases and incurable conditions such as spinal injuries, organ damage, lung disease, arthritis, diabetes, heart disease, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Lou Gehrig's disease.
| disease classification | Examples of Major Diseases |
|---|---|
| brain disease | Alzheimer's disease, stroke, Lou Gehrig's disease, Parkinson's disease, etc. |
| scalp and hair disease | Hair loss, scalp disorders, etc. |
| eye disease | Optic nerve damage, retinal damage, etc. |
| skin disease | Wrinkles, loss of skin firmness, loss of elasticity, scars, aging, etc. |
| liver disease | Cirrhosis of the liver, etc. |
| kidney trouble | Chronic renal failure, etc. |
| neurological disorder | Spinal cord injury, paraplegia, etc. |
| endocrine disorder | Diabetes mellitus, etc. |
| muscular disease | Ligamentous injuries, congenital muscle diseases, etc. |
| genital disorder | Erectile dysfunction, infertility, loss of energy, etc. |
| circulatory disease | Myocardial infarction, Buerger's disease, etc. |
| osteoarticular disease | Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc. |
Non-cultured cells (fresh stem cell therapy) vs. cultured cells
- The most important difference between fresh stem cell therapy and cultured cells is that fresh stem cells (non-cultured cells) are harvested from the patient and immediately injected into the area to be treated, making them safer and more effective. However, cultured cells are cultured for 4-6 weeks, during which time the cells become contaminated and their properties change, and no matter how many cells are grown, they are a mixture of living and dead cells, making their safety and efficacy questionable.
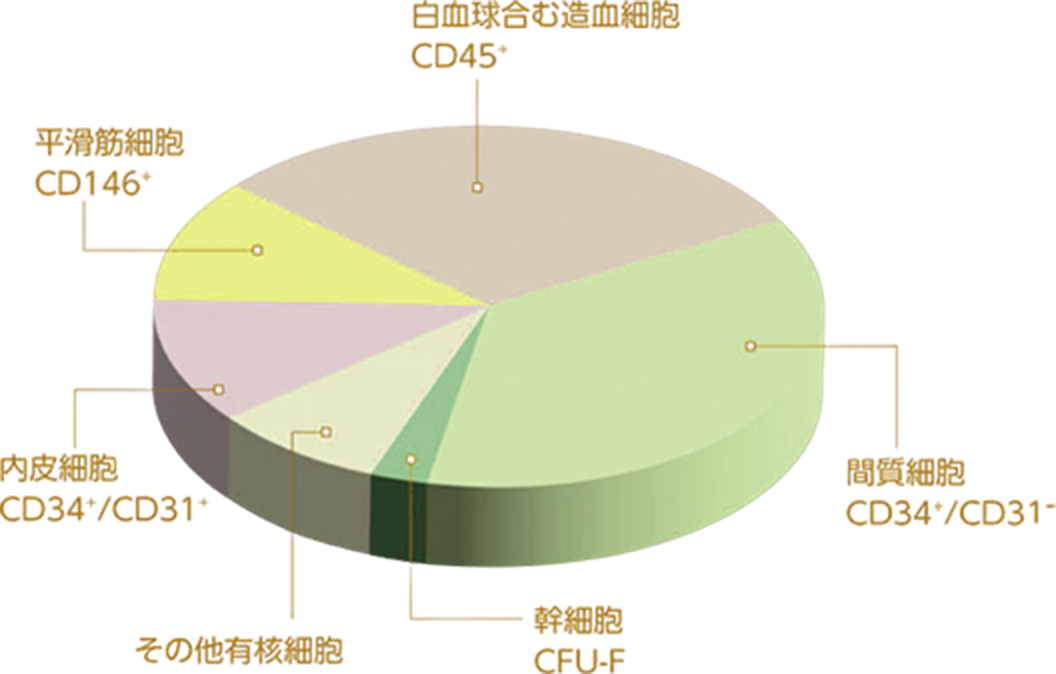
- Noncultured cells (fresh stem cell therapy) contain not only stem cells but also a miscellaneous cell population as shown in the graph. Clinically, the cells have a positive effect on the clinical efficacy of many diseases by regenerating blood vessels, reducing inflammatory effects, and repairing body tissues by taking advantage of their characteristics.
- Compared to non-cultured cells (fresh stem cell therapy), cultured cells are an open and labor-intensive processing process that involves many manual steps, and therefore, there are risks of contamination, differences in worker techniques, and cell mix-ups. In addition, workers (especially cell culturists) must be certified by the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine, and must pass a 2-day training course and written and practical examinations.
- Because all the regenerative cells are administered to the patient in real time, the entire process can be completed in a few hours without compromising the cells' unique properties.
- Conversely, cultured cells artificially alter the original properties and characteristics of cells in adipose tissue by culturing them, which involves many open, manual processes during culture and carries the risk of contamination and mix-ups, and can take up to several weeks to reach the target cell count.
- It has been confirmed that non-cultured cells (fresh stem cell therapy) have a therapeutic effect on chondrocytes by promoting anabolic prisoners and inhibiting catabolic prisoners. It has been confirmed to have a therapeutic effect on chondrocytes by promoting anabolic factors and inhibiting catabolic prisoners for knee osteoarthritis.
- In addition, it has been proven that heterologous cells such as M2 macrophages contained in non-cultured cells (fresh stem cell therapy) contribute to the therapeutic effect on cartilage cells Heterologous cells such as M2 macrophages in non-cultured cells (fresh stem cell therapy) have been shown to contribute to therapeutic effects on chondrocytes. They contribute to the therapeutic effect on chondrocytes by promoting the secretion of chondrocyte protective cytokines and growth factors.